Checkpoints
Create a reports dataset in BigQuery
/ 30
Query to pull the data for last year
/ 40
Create new data sources in Looker Studio
/ 30
Build a BI Dashboard Using Looker Studio and BigQuery
- GSP403
- Overview
- Objectives
- Setup and requirements
- Solution overview
- Task 1. Upload queryable data
- Task 2. Create a reports dataset in BigQuery
- Task 3. Query the dashboard data
- Task 4. Schedule a query in BigQuery
- Task 5. Create new data sources in Looker Studio
- Task 6. Create a new report in Looker Studio
- Congratulations!
GSP403
Overview
For as long as business intelligence (BI) has been around, visualization tools have played an important role in helping analysts and decision-makers quickly get insights from data. In this lab, you'll step into the shoes of a tree services manager for a large city. Your mission: build a powerful dashboard using Looker Studio and BigQuery to uncover valuable insights hidden within your large tree service usage logs. This dashboard will help you make informed, data-backed decisions to optimize your operations.
Why is this important? Visualizations turn raw data into actionable insights. With a well-designed dashboard, you'll quickly identify trends, spot potential issues, and make strategic choices that can improve efficiency and service quality. This lab assumes some familiarity with BigQuery and Looker Studio. For more information, review the background docs (BigQuery concepts, Looker Studio overview).
Objectives
In this lab, you will learn how to:
- Upload queryable data to BigQuery
- Create a reports dataset in BigQuery
- Run one-time queries in BigQuery and schedule queries
- Create a report in Looker Studio using BigQuery data
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account. -
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}} You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}} You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials. Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges. -
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

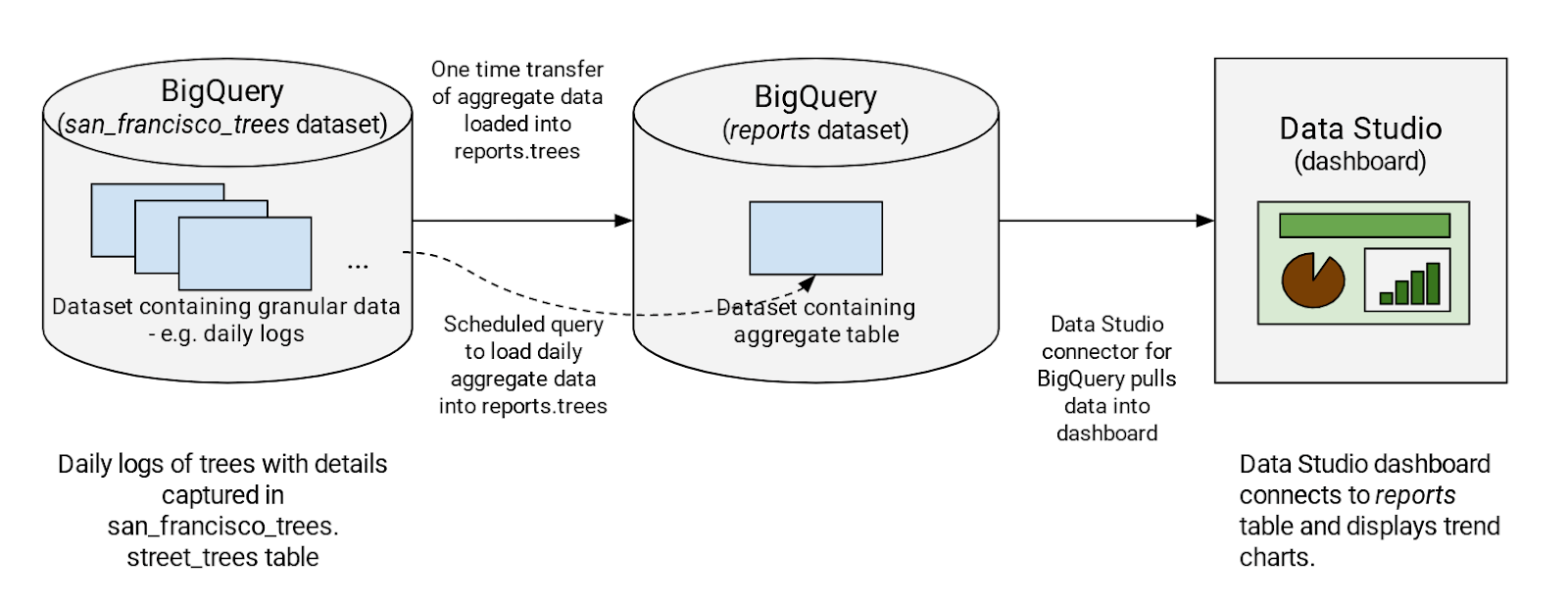
Solution overview
Typically, a dashboard shows an aggregated view of usage — it doesn't need details all the way to the level of an order ID, for instance. So, to reduce query costs, you'll first aggregate your needed logs into another dataset called "Reports" then create a table of aggregated data. You'll query the table from the Data Studio dashboard. This way, when your dashboard is refreshed, the reporting dataset queries process less data. Since usage logs from the past never change, you'll only refresh new usage data into the Reports dataset.
Task 1. Upload queryable data
In this section, you pull in some public data so you can practice running SQL commands in BigQuery.
Open the BigQuery console
- In the Google Cloud Console, select Navigation menu > BigQuery.
The Welcome to BigQuery in the Cloud Console message box opens. This message box provides a link to the quickstart guide and the release notes.
- Click Done.
The BigQuery console opens.
-
Click + ADD in the explorer section, then select Public Datasets.
-
Search for "trees" and press Enter.
-
Click on the Street Trees tile, then click View Dataset.
A new tab opens, a new project called bigquery-public-data is added to the Explorer panel:
bigquery-public-data doesn't appear to the Explorer panel, then click on + ADD > Star a project > Enter project name (bigquery-public-data) and STAR.
Task 2. Create a reports dataset in BigQuery
Next you'll create a new dataset called Reports in your project. A separate dataset has a couple of benefits: it reduces the amount of data queried by the dashboard, and it removes unnecessary access to your source datasets by users who are only interested in aggregated data.
-
Click the three dots next to your Qwiklabs project ID and select Create dataset.
-
Name your dataset Reports.
Leave the other options at their default values.
- Click Create dataset.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
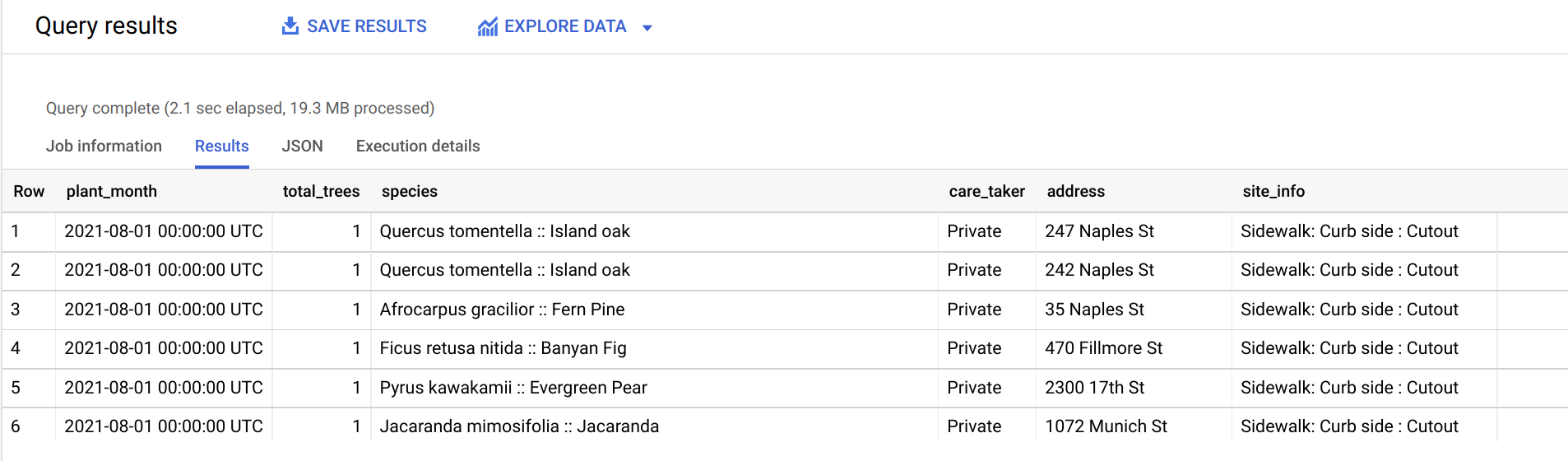
Task 3. Query the dashboard data
In this section, you will run a one-time query to pull the data for the last year, summarizing:
- The number of trees planted each month
- Which species of trees were planted
- Who the caretaker of the trees is
- Address of the planted trees
- Tree site information
-
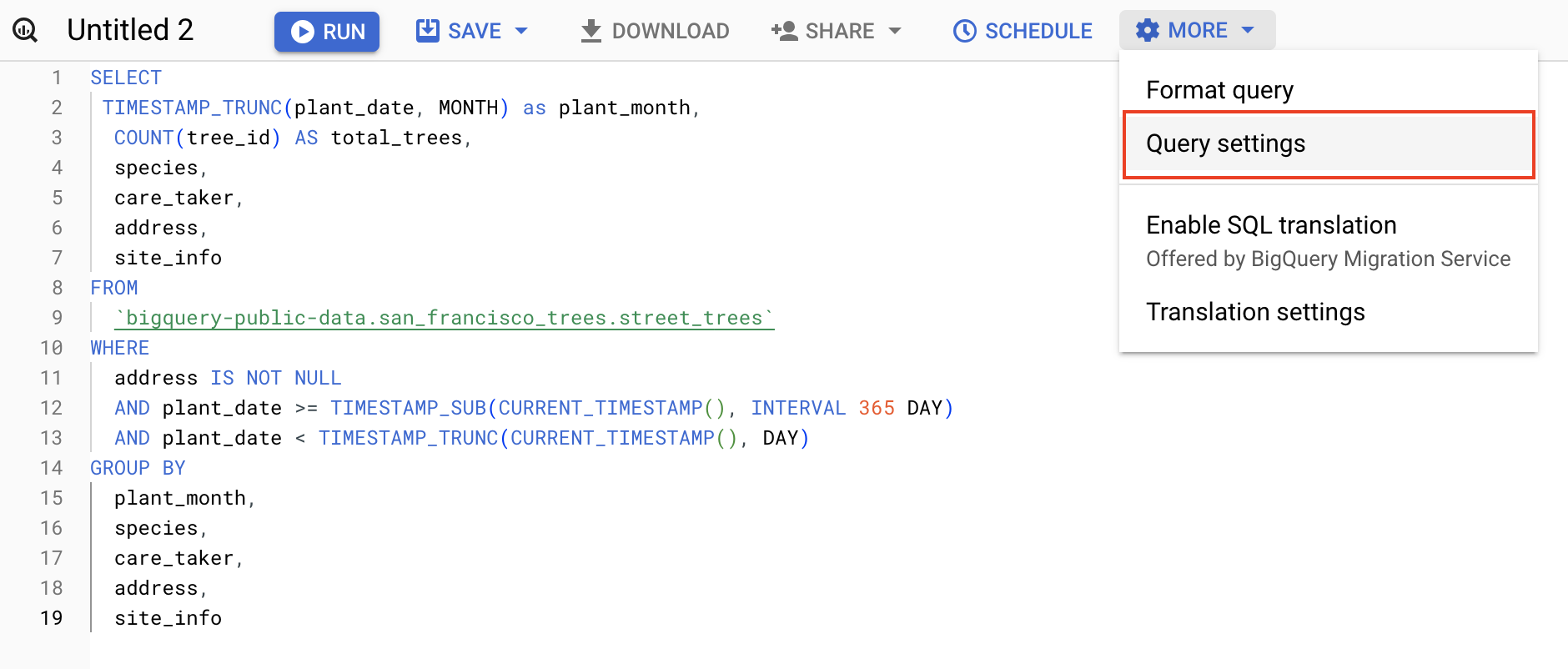
Open the Query editor by clicking the + button on the top of the BigQuery Console.
-
Add the following to the Query Editor:
- Click the More button, and select Query settings from the dropdown menu.
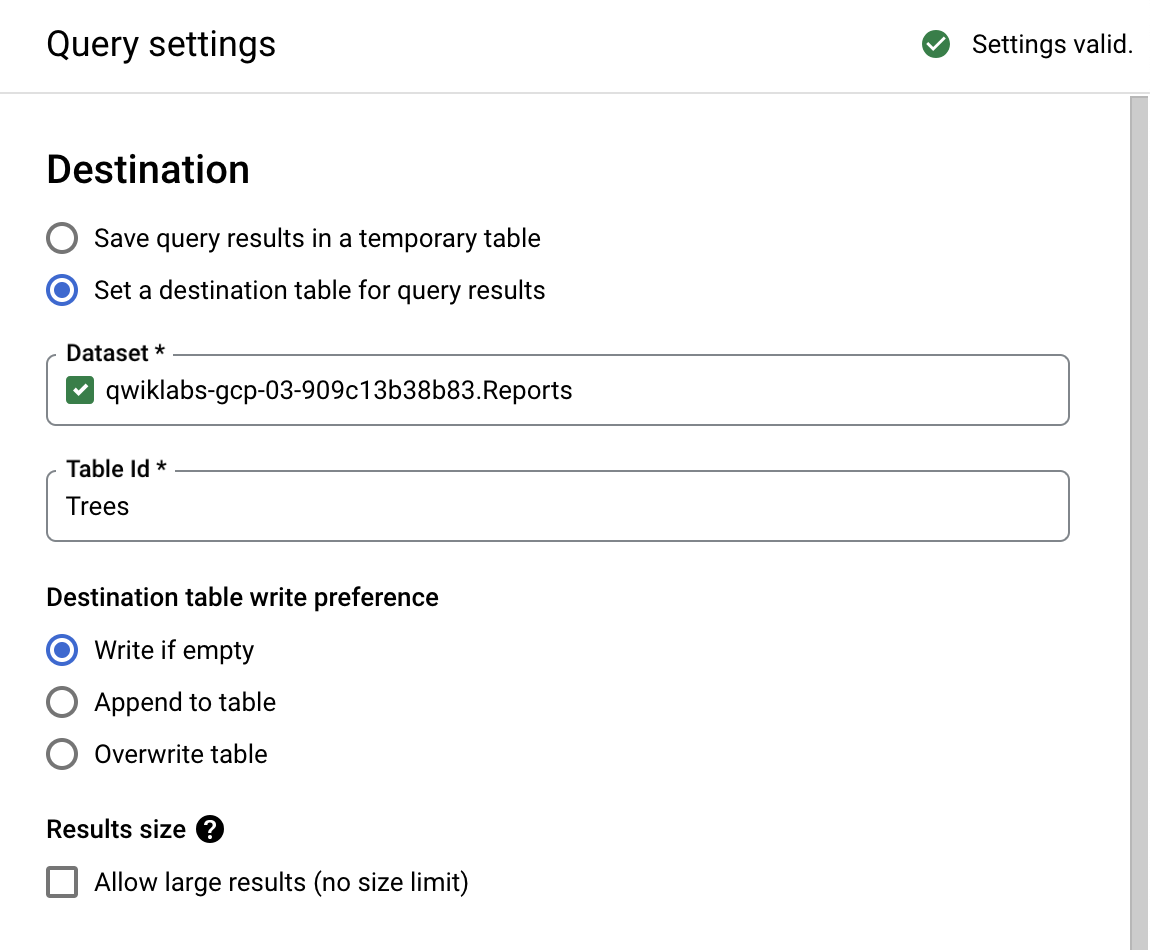
- Select Set a destination table for query results.
- For Dataset name, type
Reports. Select the Reports dataset you created earlier. - For Table Id, type
Trees. - For Destination table write preference, select Write if empty.
Because you specified a Table name and selected the Write if empty preference, the query creates a table if the table does not already exist.
-
Accept the other default settings and click Save.
-
Click Run to run the query.
When the query completes, you are on the Results tab, where you can see the data.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
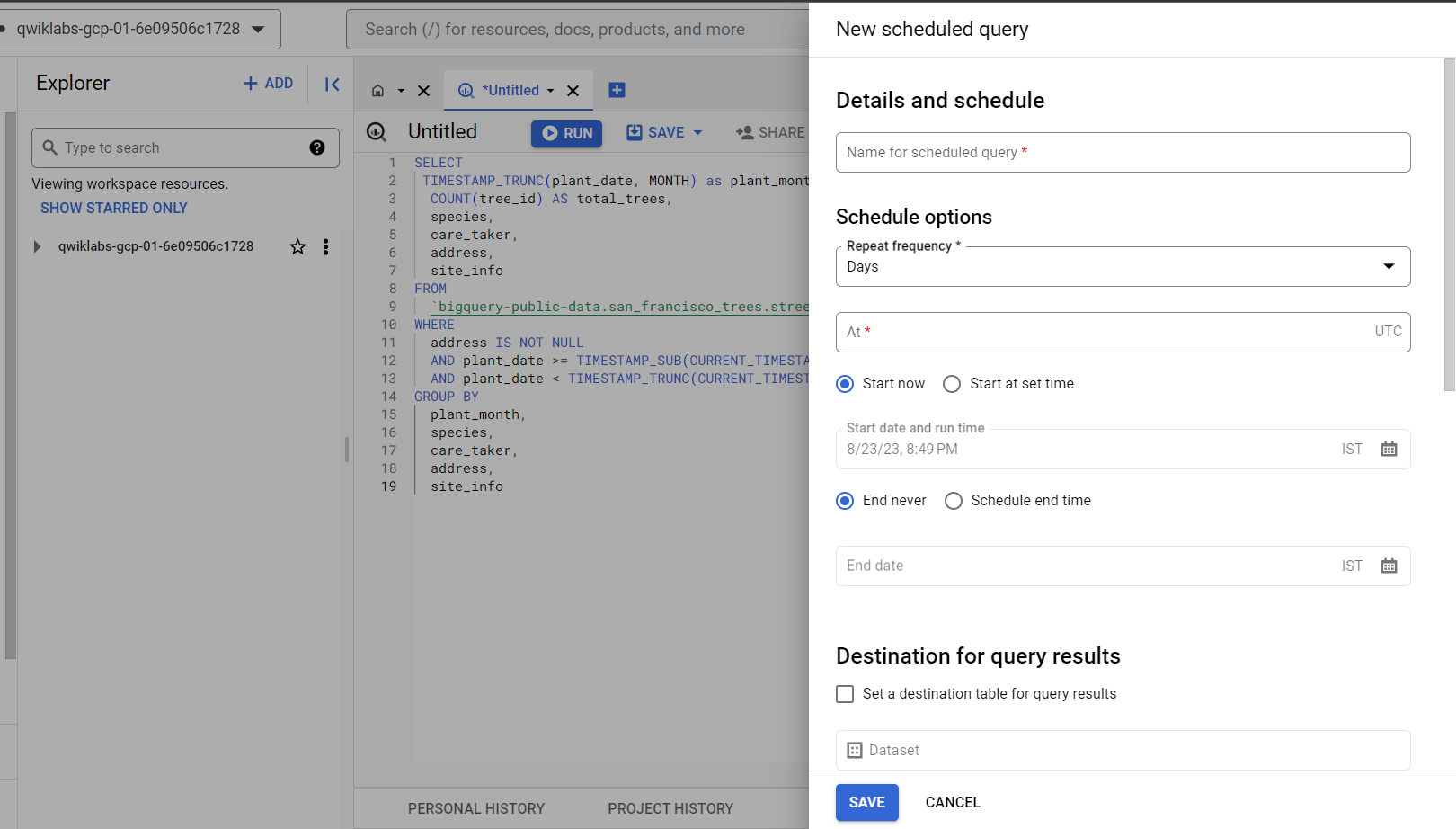
Task 4. Schedule a query in BigQuery
To keep your dashboard up-to-date, you can schedule queries to run on a recurring basis. Scheduled queries must be written in standard SQL, which can include Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. The query string and destination table can be parameterized, allowing you to organize query results by date and time.
Now you add a query that checks each day for new data. When new trees are planted, you'll get the additional stats updated directly into the reports.trees table.
- Open a new Query Editor tab and run the following query to pull incremental data into the
reports.treestable on a daily basis using the scheduled query feature:
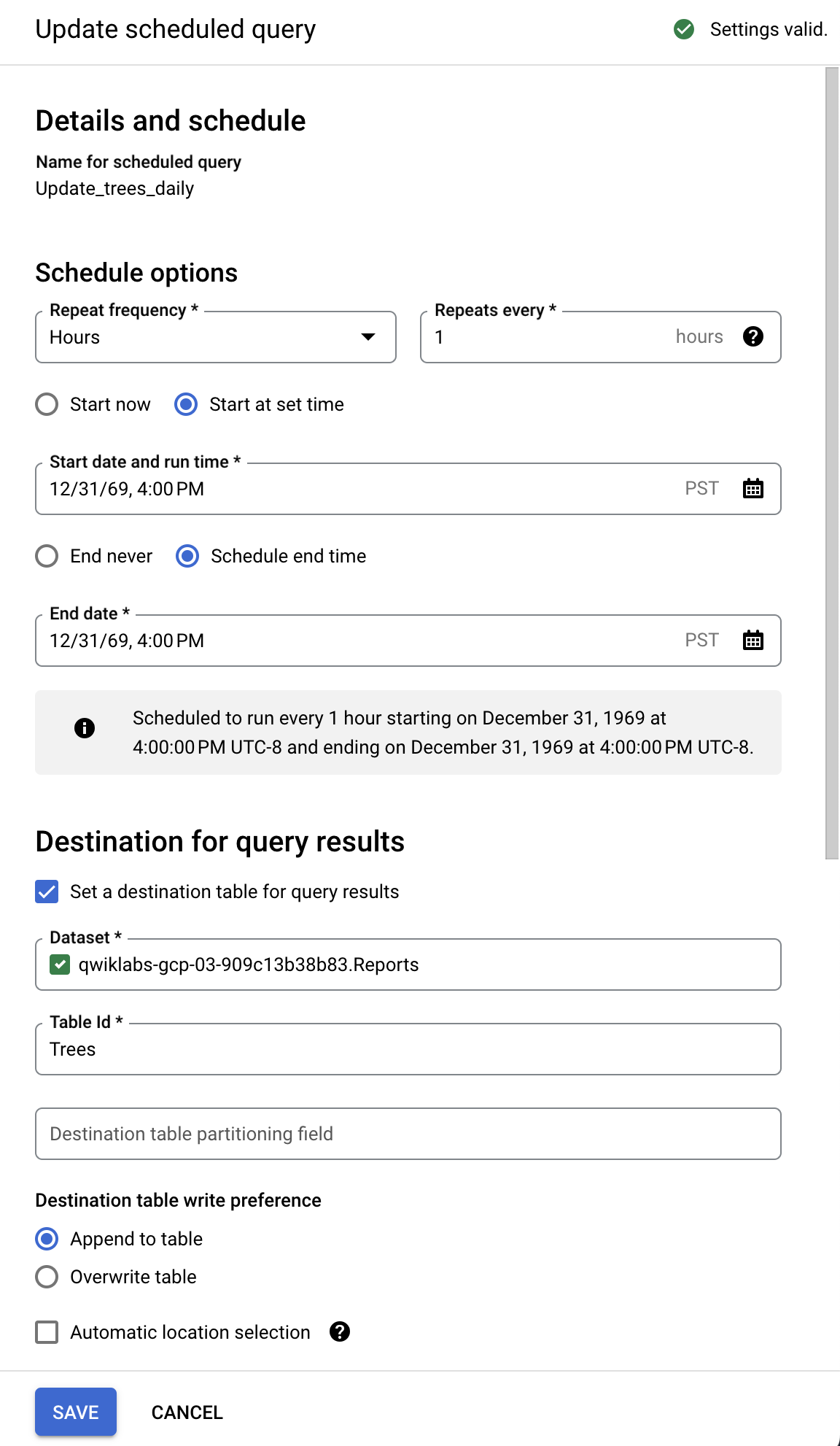
- Click on the Schedule button, and New scheduled query page opens.
- On the new Scheduled query page, set the following:
-
Name: Update_trees_daily
-
Schedule options:
- Repeat frequency: Click the dropdown and select Hours.
- Repeats every: 1 hour
- In the Destination for query results sections, check the box for Set a destination table for query results and specify dataset name as
Reports.
- Table name: type in "Trees" and select Append to table for Destination table write preference so it doesn't overwrite existing data.
-
Click Save.
-
You may have a popup blocker enabled, click Allow and then give your lab credentials permission, then agree to replace your query.
Task 5. Create new data sources in Looker Studio
Now you'll build your dashboard using the tree data you've just aggregated with Looker Studio.
-
Open a new tab in your browser and go to Looker Studio.
-
Click Create in the top left, and then click Report.
-
Enter the country and check the terms and conditions.
-
Click Continue.
-
Select No for all email offers, and then click Continue.
Task 6. Create a new report in Looker Studio
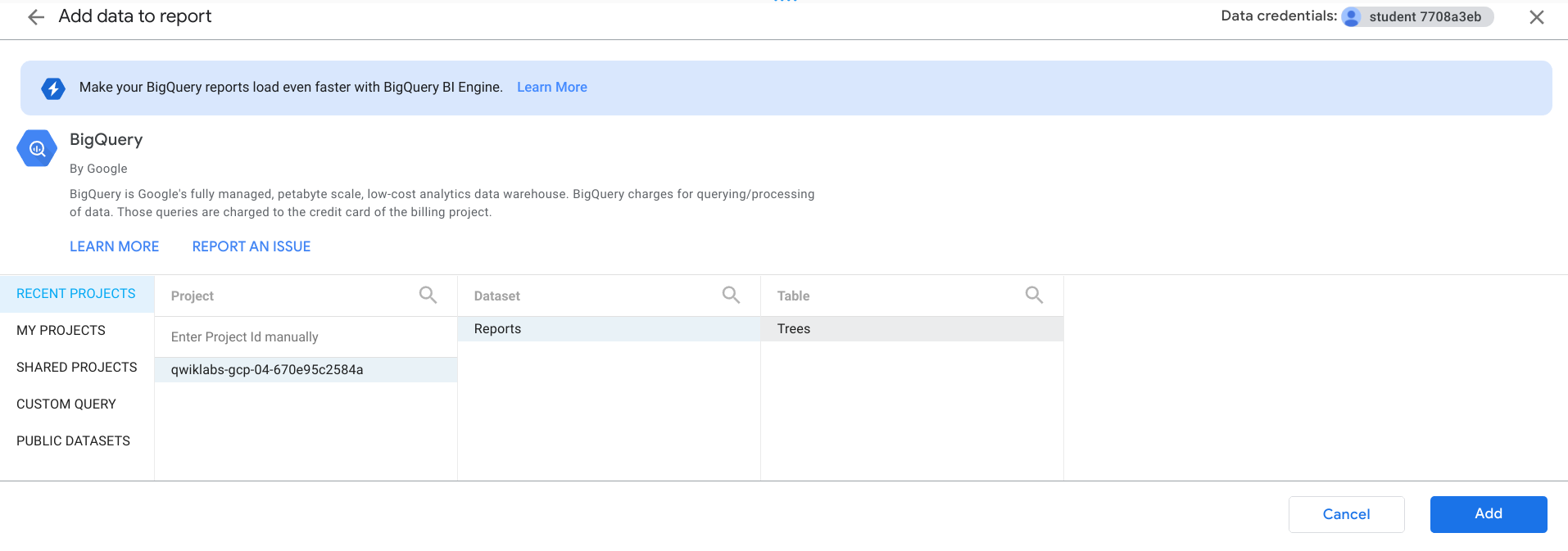
- Click on the BigQuery, then click Authorize.
Now you'll use the BigQuery connector to connect to the reports.trees table.
- Start by selecting your Qwiklabs project, then the Reports dataset, then the Trees table, as shown below:
- Click Add and then click Add to Report.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Now you can create charts using the data in this table.
-
Click on Add a chart dropdown and select the type you want. In this example, you can see the following types of charts:
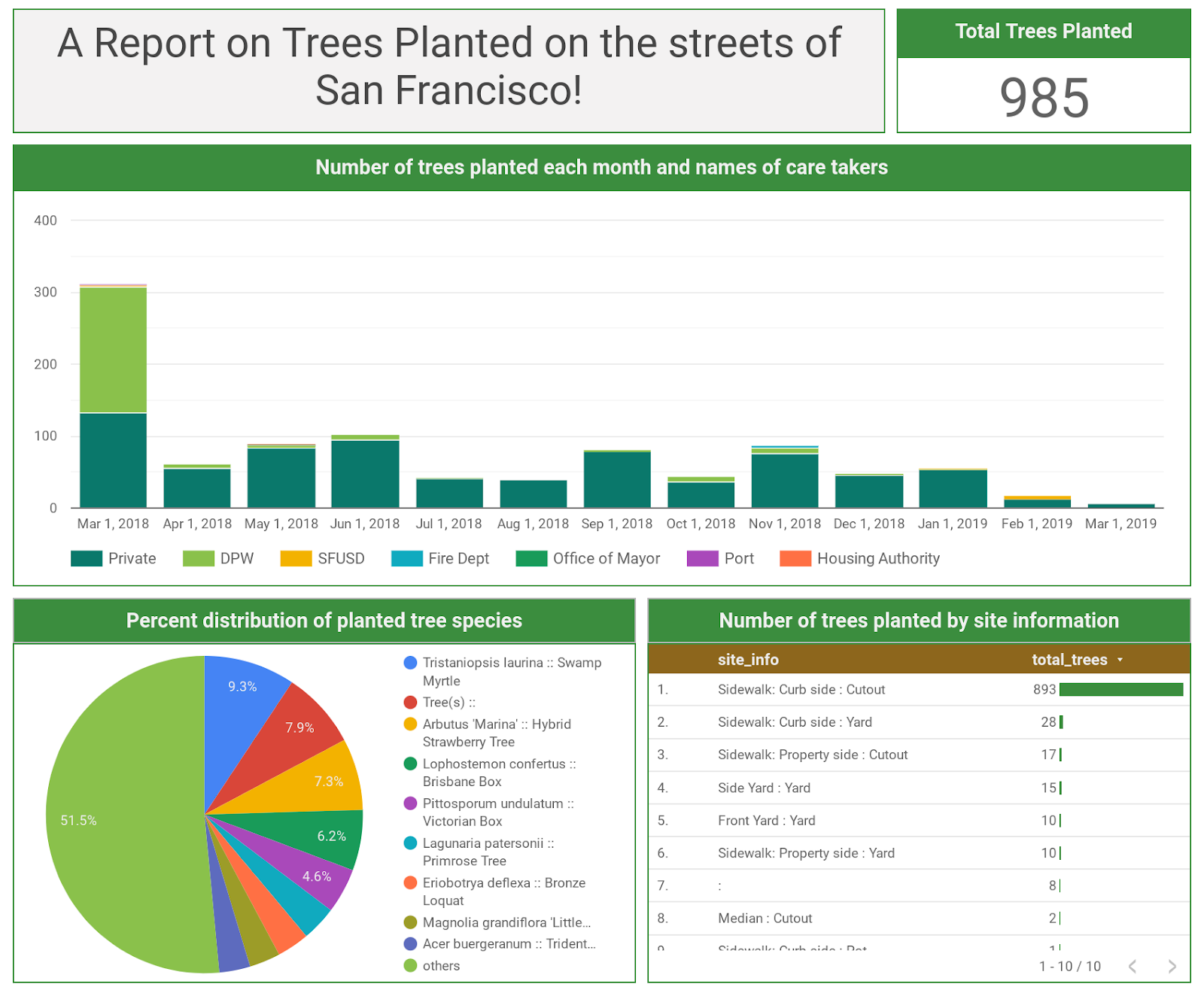
- Stacked column bar graph showing the number of trees planted each month and the name of the caretaker who planted them.
- A scorecard showing the total number of trees added in the last year.
- A pie chart showing the percent distribution of trees planted by their species.
- A table chart along with a bar graph representing the number of trees planted by site.
You can experiment on your own creating charts and titles modeled after the example. Here are some hints:
- Titles are created using the text tool. In the example, titles were created for each chart and the dashboard itself.
- When a chart is selected, you can edit the colors and font sizes when you click on the Style tab on the right-hand side.
- Click on a chart to modify its size and drag it to a new location.
Congratulations!
Congratulations! In this lab, you learned how to build a BI dashboard for visualizing patterns in your business data with less risk of expensive query volumes. You created a dataset in BigQuery, ran a one-time query, scheduled a query, and created a report in Looker Studio. You can now use these skills to build your own BI dashboard with Looker Studio and BigQuery!
Next steps / learn more
- This lab is based upon this blog post by Pradnya Khadapkar
- Visualizing BigQuery data using Looker Studio
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated April 02, 2024
Lab Last Tested April 02, 2024
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.